Program Structure & Courses
The Financial Economics study program builds upon a strong foundation in economic theory, econometrics, and quantitative finance. This master's prepares students for challenging future careers in the private and public sectors of economies worldwide, including the banks and stock exchanges as well as for scholarly research endeavors.
The program consists of compulsory modules in the first two semesters, compulsory elective modules, a master's seminar, a scientific project, and lastly, the master's thesis in conjunction with a research seminar.
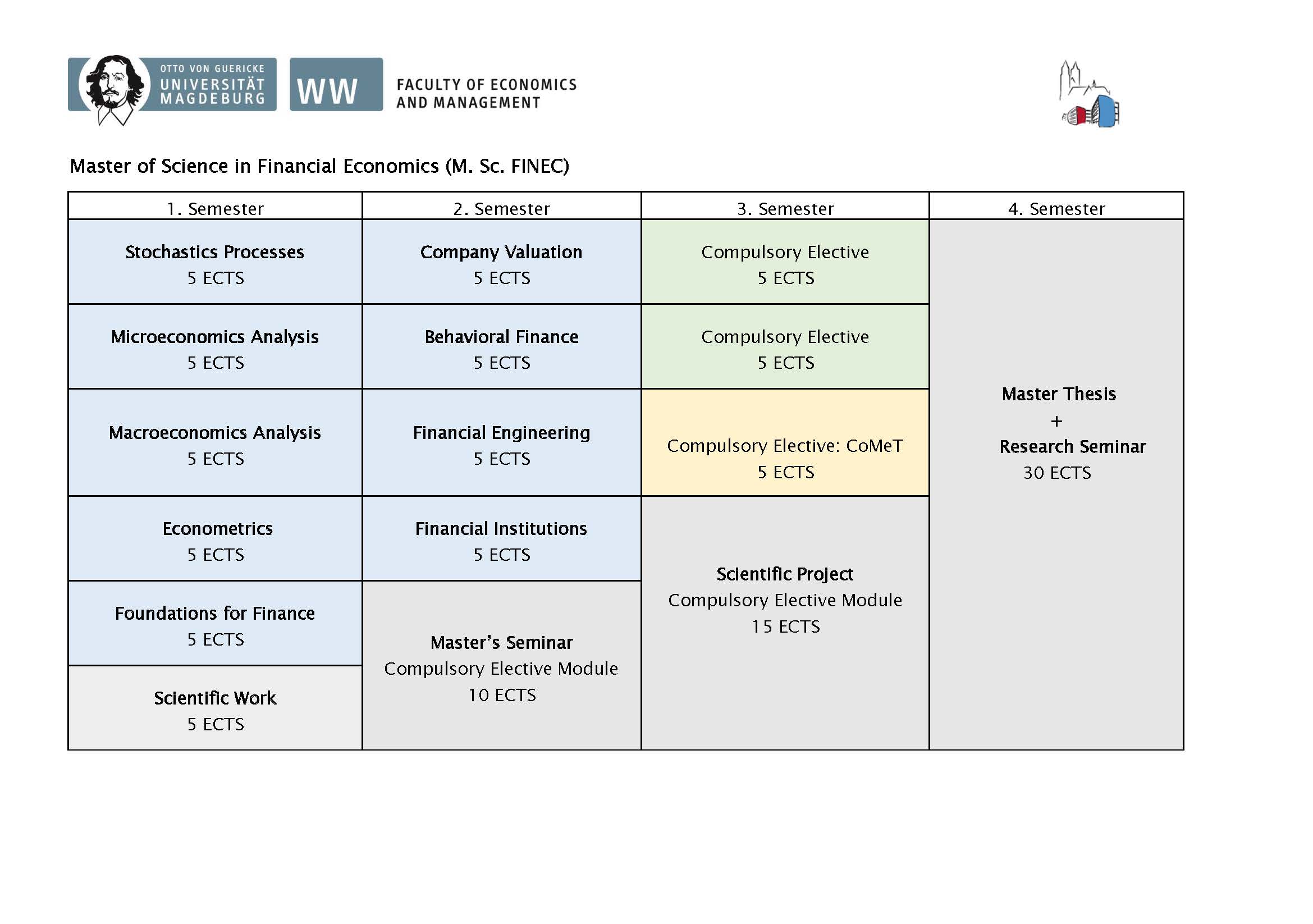
First Semester
In this course, students get to know stochastic calculus like Brownian motion, conditional expectation, martingale, Ito stochastic integral, Ito lemma, and Ito stochastic linear differential equation and shall obtain competencies to understand some main ideas and apply tools of stochastic calculus.
With Econometrics, students shall improve upon already established knowledge of fundamental econometric methods, learn about concepts of modern micro-econometric methods during lectures, and independently become acquainted with a state-of-the-art methodology by studying the recommended literature, are able to use STATA to solve problems, and analyze real-world problems independently.
In this module, students shall acquire an analytical understanding of the determinants of individual decisions, develop a thorough understanding of the consequences of decentralized decision-making for individual and firm behavior in partial equilibrium models, and analyze the existence, stability, and efficiency properties of general equilibria.
In this course, students acquire knowledge of the empirics of growth and business cycles, develop a thorough understanding of the basic models of economic growth, are able to identify the sources and amplifiers of aggregate fluctuations, and are empowered to study macroeconomic models independently and self-reliantly.
With Foundations for Finance, students acquire knowledge about valuation models in finance, have the ability to make simple portfolio decisions, and develop an understanding of firms’ major financial decisions.
Compulsory Elective Module: Academic Methods, 5 ECTS
A. Academic Writing and Presentations
Students:
- critically evaluate and distinguish academic and non-academic materials,
- gain further insights into academic methodology and argument structure,
- improve skills in presenting an argument in an appropriate written and oral form according to accepted norms,
- enhance their linguistic competence in subject-specific language.
or
B. Quantitative Approaches
Students:
- acquire a broad knowledge in academic research, empirical analysis and model development,
- become acquainted with common research tools and academic software,
- develop an experience with working in a group and presenting their solution.
Second Semester
In this course, students shall acquire a broad theory-based knowledge of company valuation techniques in different frameworks, become acquainted with finance software (e.g. Excel, MATLAB), develop an understanding of and experience with empirical analysis based on real data, and gain insights into valuation pitfalls and recent models.
With Behavioral Finance, students acquire knowledge about market and portfolio anomalies, are enabled to apply techniques how to detect these anomalies, gain insight into psychological explanations, and get to know models in Behavioral Finance.
In this module, students shall become acquainted with the most relevant concepts for the modelling of derivatives (financial options and real options), develop an adequate understanding of the methods for deriving the price of options, gain insights into computer algebra systems during the teaching unit, are able to choose feasible analytical numerical algorithms and apply them to problems of Corporate Finance at the end of the teaching unit, and acquire team and communicative competence through group projects.
With Financial Institutions, students shall acquire the ability to use economic reasoning to analyze the structure of financial markets, describe the institutional frameworks in which intermediaries and central banks operate, analyze how a bank conducts business using the simulation game “ProBanker”, present and defend management decisions taken in the simulation game, present a solution that has been developed through teamwork in the classroom, and are encouraged and empowered to work independently and self-reliantly.
Compulsory Elective Master's Seminar, 10 ECTS
Choose one of the offered seminars, for example:
A. Computational Finance and Financial Management
Students become familiar with modeling tools for financial options and option pricing, acquire basics in generating random numbers with specific distributions, learn to perform a Monte Carlo simulation, and develop an understanding of numerical methods e.g. the finite element method, have the ability to solve financial problems in programming languages e.g. Python, Matlab, improve skills to present and defend their work.
This seminar is oriented toward current developments in the fields of computational finance and financial management.
or
B. Microeconometric Tools for Labor Market Research and Policy Evaluation
Students acquire knowledge of advanced problems of empirical labor economics and related fields independently, learn techniques to derive causal statements from observational data, develop the ability to critically discuss scientific papers, acquire presentation skills, and develop the ability to independently write a seminar paper.
or
C. Topics in Economic Analysis of Law
Students learn how to identify and describe problems and challenges for theoretical reasoning, get to know academic research methods and sources of information, acquire the ability to write academic papers and present their results, participate in academic discussions.
Note: For the seminars, we have the following regulations and procedures:Pre-registration a semester ahead required!
During the first session of this seminar guidelines for academic writing will be introduced. Seminars are supervised by a professor.
Students have to write a seminar paper on the economic analysis of legal rules and their relation to management problems. The written paper must be defended in class.
Third Semester
Compulsory Electives (Specialization), 15 ECTS in total to obtain
choose from the offered modules offered, for example:
A. Behavioral Finance, 5 ECTS
Students acquire knowledge about market and portfolio anomalies, are enabled to apply techniques how to detect these anomalies, gain insight into psychological explanations and get to know models in Behavioral Finance.
B. Company Valuation, 5 ECTS
Students acquire a broad theory-based knowledge of company valuation techniques in different frameworks, become acquainted with finance software (e.g. Excel, MATLAB), develop an understanding of and experience with empirical analysis based on real data, and gain insights into valuation pitfalls and recent models.
C. Downside Risk, 5 ECTS
Students obtain a comprehensive theory-based knowledge of downside-oriented portfolio management, become familiar with finance software (e.g. Excel, MATLAB), and, thus, are able to conduct empirical analysis in the field of downside risk.
D. Economics of Growth, 10 ECTS
Students become acquainted with the recent advances in the theory and empirics of economic growth and long-run economic development, learn to master the relevant modeling techniques of dynamic economic analysis, gain a deeper understanding of the policy-relevant factors driving economic growth, and develop the ability to starting their own research on economic growth.
E. Monetary Economics, 5 ECTS
Students get introduced to the fundamentals of financial markets and monetary systems, become acquainted with different monetary aggregates and financial assets, gain insight into typical problems like deriving yield- or risk structures of interest rates, acquire knowledge about central bank systems, are enabled to cope with problems of money supply and interbank transactions.
F. Population and Family Economics, 5 ECTS
Students learn what economists have to say about individual decisions to marry, procreate, etc., become acquainted with topics and tools of quantitative economic analysis, acquire a profound knowledge of the empirics of marriage and fertility decisions, develop an understanding of the incentive structures within and around families, acquire knowledge how to evaluate policy measures targeted at demographic outcomes.
... will be filled in as soon as the module description is published
Compulsory Elective Scientific Project (Specialization), 15 ECTS
choose from one of the offered options, for example:
A. Cost of Equity – Model-based Estimation vs. Actual Cash Flows
Students gain knowledge of basic and state-of-the-art research on cost-of-capital modeling and computations, develop the competence to prepare, comprehend and discuss relevant literature, are capable to prepare and analyze data, learn to efficiently present their empirical results to a group of peers, study classical cost of equity estimation models, asset pricing theory, study and apply financial data analysis.
B. FinTech and Blockchain Innovations
Students acquire knowledge of how to build financial models, experience how to implement the models in programming languages e.g. Python, and Matlab, learn how to practically apply financial modeling tools to a concrete real-world problem, develop an understanding of creating virtual and/or physical prototypes to test and visualize their ideas, gain insights in the young and innovative field of FinTech and Blockchain, improve skills to present and defend their work.
This Scientific Project is oriented toward current developments in the fields of FinTech and Blockchain innovations.
Students expand their hands-on and interdisciplinary abilities by developing individual solutions to a self-chosen topic in the fields of financial modeling and forecasting, risk management, and financial technologies based on e.g. Blockchain technology.
C. International Tax Planning and Firm Value
Students gain knowledge on current international research in the field of taxation and firm valuation with a focus on tax avoidance and (tax) risk, learn how to specify a research question and how to acquire knowledge in an emerging field of research by themselves, gain experience how to write a seminar thesis, including an extensive literature review, and presentation of results, intensify their skills on statistical research methods and how these methods are used in empirical tax research, analyze of current research on the nexus of tax avoidance, firm value, and risk. The main topic is how taxes avoidance activities and tax aggressiveness affect the market capitalization of firms on stock markets, analysis of research questions including the association of tax avoidance activities and market capitalization, the measurement of tax aggressiveness as well as the identification of causal relationships, discuss how the association of tax avoidance and firm value depends on risk and corporate governance.
D. Empirical Behavioral Management Research
Students understand what biases chief executive officers (CEOs) exhibit and how these influence their behavior and firm strategy, develop a profound understanding of the latest empirical methods to analyze behavioral executive biases, learn how to use the statistical program Stata, master recent empirical methodology to identify statistical effects, derive recommendations: How should the CEOs of the future look like and what should they consider in his decision making?
This project seminar captures the current state of research on CEO biases and aims to prepare students for related master theses. Relying on the upper echelon's view, a focus will lie on how CEO biases reflect in firm strategy. The module offers a basic course on applied statistics since it will be relevant for the data analysis of CEO biases. The course relies on current insights from empirical research and applies them to practical challenges. Participants will solve issues based on a literature review as well as quantitative modeling and synthesize related insights into leadership recommendations. This seminar will require team collaboration. Applicants are expected to show a high interest in quantitative problem-solving. Additionally, the course will contain workshops to prepare students for practice.
Study Abroad
Although a semester abroad is not mandatory, the Faculty of Economics and Management highly recommends that FINEC students take advantage of a semester abroad at one of our many cooperation universities worldwide. Students interested in going abroad must begin the application procedure one year (two semesters) in advance (e.g. third semester abroad; consultation and application in first semester).
For a complete overview of our cooperation schools, please click here and filter your search according to faculty and study program.
For more information on different programs, such as ERASMUS, Free Mover, and WORLDWIDE, please click here.
Besides the possibility of a study-abroad semester at one of our cooperation schools, students may also do an internship abroad for one semester.
Student counseling and internship/job fair (annually in October) on campus available
For more information regarding an internship abroad, please click here.
Fourth Semester
Master Thesis and Final Seminar, 30 ECTS
With this final seminar and a written thesis, students develop the ability to find and define a research project, gain insight into the planning and realization of their own research project, acquire the ability to write and present a research paper, and acquire the ability to academically discuss other students’ research.
This final master's program module is organized as a research colloquium, where students have to present the first results of their projects and discuss open questions.
The thesis project has a scientific or applied research focus. Cooperation with firms or other organizations is possible.
The proceeding time for the master's thesis is strictly regulated. From the registration, issuing the topic and the submission is in total and a row five months (including four weeks of reading time).
Students define and realize a research project, present the (preliminary) results of their research, write their Master’s Thesis, and present and defend the result in the final seminar (presentation).
Applicants and enrolled students must be prepared with their undergraduate degrees to be able to take part in our master's courses. This master's program is established on the bachelor's program of our school. Preparatory courses are not available. For further information about the content and objectives of the bachelor's program, please check out the module handbook descriptions here.
